The TCSG Framework: Empowering Full-Stack Innovators in the Age of AI
On This Page
- Introduction
- What is the TCSG Framework?
- The Professional DNA of a Full-Stack Innovator
- Deep Dive into TCSG Dimensions
- Technology (T)
- Creativity (C)
- Strategy (S)
- Growth (G)
- TCSG Overlaps and Combinations
- Technology & Creativity (T&C): Innovative Design
- Creativity & Strategy (C&S): Visionary Planning
- Strategy & Growth (S&G): Scalable Solutions
- Growth & Technology (G&T): Data-Driven Optimization
- Full-Stack Innovation: The Central Overlap (T&C&S&G)
- Developing TCSG Skills: A Roadmap for Full-Stack Innovators
- Technology Dimension Proficiency Levels
- Creativity Dimension Proficiency Levels
- Strategy Dimension Proficiency Levels
- Growth Dimension Proficiency Levels
- Implementing the TCSG Framework in Your Organization
- The Future of Work: TCSG and AI Augmentation
- Conclusion
Learn to become a Full-Stack Innovator
AdvancedSummary
This post introduces the TCSG Framework, a comprehensive approach to developing the skills needed to thrive as a full-stack innovator in the age of AI.
Target Audience
This article is suitable for advanced AI explorers.
Key Takeaways
- Master the four dimensions of innovation: Technology, Creativity, Strategy, and Growth.
- Learn how to develop and integrate skills across all TCSG dimensions.
- Discover how to leverage the TCSG Framework to drive innovation in an AI-augmented world.
Listen to the NotebookLM podcasters break the TCSG framework down into bite-sized conversation. (This riveting podcast is AI-generated.)
Introduction
As new advanced language models continue to push the boundaries of what we thought was possible in AI, the professional skill stack is being turned on its head.
In 2024, putting your career on the fast track with AI means mastering the New Skill Stack.
The ability to innovate and operate across multiple domains is now more crucial than ever. As artificial intelligence continues to reshape industries and redefine the nature of work, a new breed of professional is emerging: the full-stack innovator, an augmented generalist with well-developed competencies across every key professional area.
These individuals possess a unique blend of skills that allows them to navigate the complex intersection of technology, creativity, strategy, and growth.
But what exactly is a full-stack innovator, and how can aspiring professionals develop the necessary skills to thrive in this role?
Enter my TCSG Framework – a comprehensive approach to understanding and cultivating the key dimensions that define these cross-disciplinary change-makers.
Let’s start by outlining the framework and why it’s essential to consider.
What is the TCSG Framework?
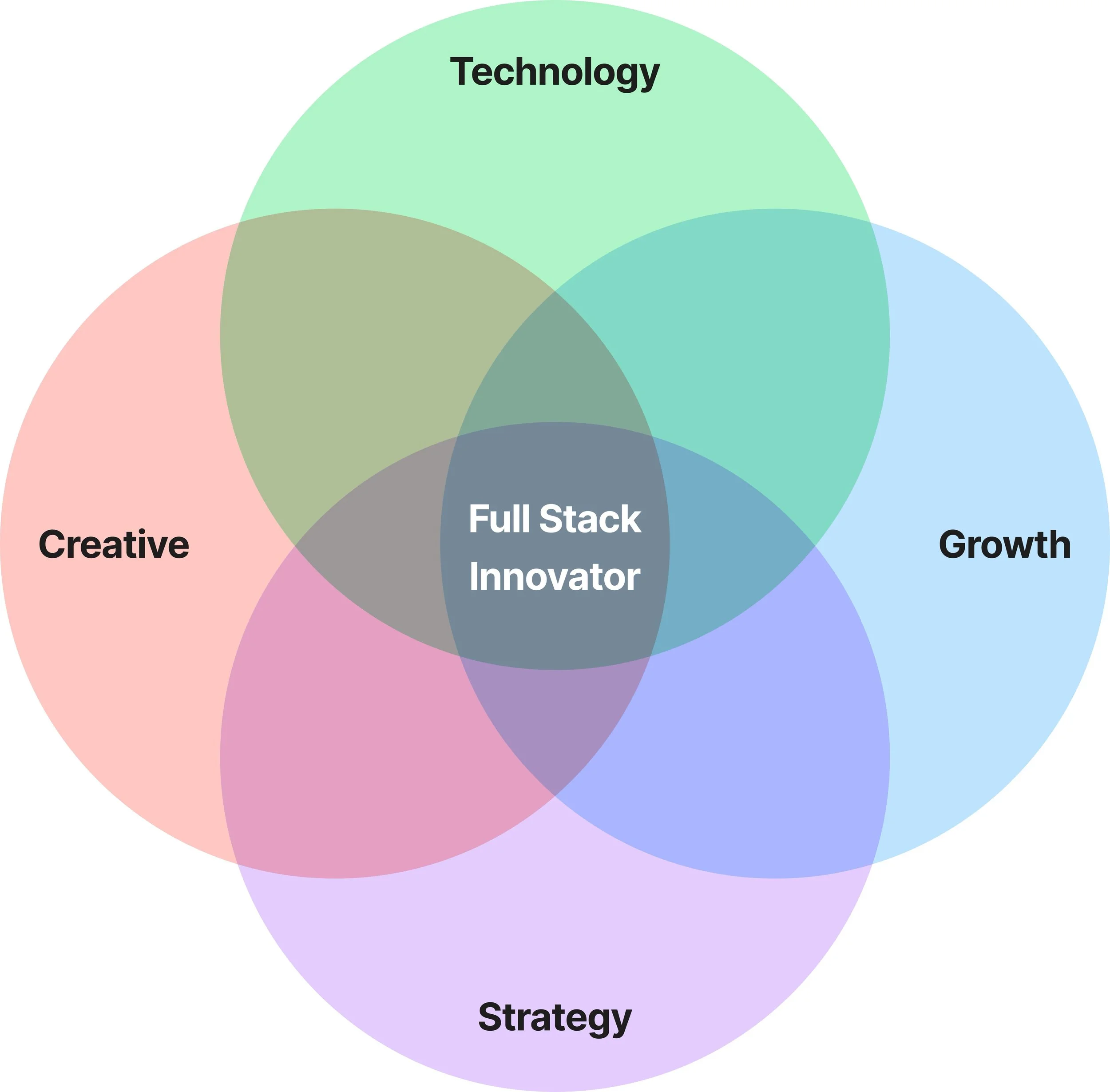
The TCSG Framework is a skills and competency model I’ve developed that outlines the critical dimensions needed to excel in today's innovation-driven economy.
It stands for Technology, Creativity, Strategy, and Growth – four interconnected areas that form the foundation of a full-stack innovator's toolkit.
Let's briefly explore each dimension:
Technology (T): Proficiency in leveraging cutting-edge tools, platforms, and methodologies to solve problems and create value.
Creativity (C): The ability to generate novel ideas, reframe challenges, and design innovative solutions that meet user needs and market demands.
Strategy (S): Skill in analyzing complex systems, making data-driven decisions, and developing robust plans to achieve long-term objectives.
Growth (G): Aptitude for identifying and capitalizing on opportunities, driving measurable results, and scaling impact in a sustainable manner.
By integrating these four dimensions, the TCSG Framework provides a structured approach to understanding, assessing, and developing the critical skills needed to navigate complex challenges and seize emerging opportunities in our AI-driven world.
The Professional DNA of a Full-Stack Innovator
Before we dive deeper into each dimension of the TCSG Framework, it's essential to understand the holistic profile of a full-stack innovator. These professionals possess a unique "professional DNA" that sets them apart in the innovation ecosystem. Key components of this DNA include:
Technical Expertise: A strong foundation across various technologies, including software development, data analysis, and emerging fields like AI and blockchain. Full-stack innovators can work comfortably with different parts of the technology stack.
Business Acumen: A solid understanding of business models, market dynamics, customer needs, and financial considerations. This allows them to identify opportunities and create compelling value propositions.
Design Thinking: A human-centered approach to problem-solving, encompassing skills in user research, prototyping, and iterative design. Full-stack innovators excel at creating intuitive and compelling user experiences.
Entrepreneurial Mindset: Comfort with ambiguity, risk-taking, and rapid experimentation. They display resilience in the face of setbacks and can pivot when needed, driven by a passion for creating something new and making an impact.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: The ability to work effectively with diverse teams across engineering, product, design, marketing, and other functions. Strong communication and leadership skills are crucial for aligning stakeholders around a shared vision.
Continuous Learning: An insatiable curiosity and commitment to staying up-to-date with the latest industry trends, technologies, and best practices. Full-stack innovators learn from failures and adapt based on new insights.
Systems Thinking: The capacity to understand complex systems and how different parts interact. They consider second-order effects and unintended consequences when designing solutions.
Creativity and Vision: The imagination to envision new possibilities and novel ways to solve problems. Full-stack innovators challenge assumptions and status quo thinking, inspiring others to rally around ambitious goals.
The TCSG Framework builds upon this professional DNA, providing a structured approach to developing and honing these critical skills. By mastering the four key dimensions of Technology, Creativity, Strategy, and Growth, aspiring innovators can cultivate the diverse skill set needed to drive breakthrough innovations from concept to successful commercialization.
Deep Dive into TCSG Dimensions
Technology (T)
In the age of AI and rapid technological advancement, the Technology dimension of the TCSG Framework is more critical than ever. It encompasses not only technical skills but also the mindset and behaviors that enable full-stack innovators to leverage technology effectively.
Key components of the Technology dimension include:
Analytical Thinking: The ability to break down complex problems and systems into manageable components, coupled with strong logical reasoning and structured analysis skills.
Tool and System Proficiency: Ease of use with various software applications, devices, and platforms, along with the ability to quickly learn and adapt to new technologies. This includes understanding how different tools and systems integrate and operate together.
Problem-Solving Orientation: A natural inclination to leverage technology in finding solutions, associating challenges with potential technological approaches, and seeing technology as an enabler for problem-solving.
To develop strength in the Technology dimension, full-stack innovators engage in behaviors such as:
Actively exploring new technologies through research and experimentation
Optimizing processes and workflows using technological solutions
Analyzing data to derive actionable insights that guide decision-making
By cultivating these skills and behaviors, full-stack innovators position themselves at the forefront of technological innovation, ready to harness the power of AI and other emerging technologies to drive transformative change.
Creativity (C)
While technology provides the tools, creativity fuels the innovation process. The Creativity dimension of the TCSG Framework is essential for generating novel ideas, reframing challenges, and designing solutions that resonate with users and markets.
Key components of the Creativity dimension include:
Imaginative Thinking: The ability to conceive original ideas and concepts, coupled with the mental flexibility to explore creative possibilities and "think outside the box."
Open-Mindedness: A receptivity to unconventional or atypical approaches, willingness to consider diverse perspectives, and comfort with ambiguity and lack of obvious solutions.
Artistic and Aesthetic Sense: An appreciation for creative and artistic expression, coupled with an eye for design, form, and aesthetic appeal.
Full-stack innovators strengthen their creative muscles through behaviors such as:
Generating a high volume of original ideas through techniques like brainstorming
Challenging conventional norms and proposing alternative perspectives
Pursuing artistic and creative endeavors outside their primary field of work
By developing their creative capabilities, full-stack innovators enhance their ability to approach problems from unique angles, leading to breakthrough solutions that set them apart in the innovation landscape.
Strategy (S)
The Strategy dimension of the TCSG Framework is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of innovation and ensuring that technological and creative efforts are aligned with long-term objectives. It provides the roadmap for turning innovative ideas into reality.
Key components of the Strategy dimension include:
Systems-Level Thinking: The aptitude for recognizing patterns and connections, understanding complex, interdependent variables, and synthesizing disparate elements into unified wholes.
Long-Term Vision: The ability to project and anticipate future states and scenarios, coupled with a natural inclination towards long-range planning and identifying potential implications and consequences.
Sound Decision-Making: The capability to judiciously evaluate alternatives and trade-offs, process data rationally to arrive at optimal choices, and weigh pros and cons to make difficult decisions.
Full-stack innovators strengthen their strategic capabilities through behaviors such as:
Developing detailed plans and strategies with concrete goals and milestones
Navigating stakeholder dynamics by managing diverse interests and building consensus
Executing strategic initiatives by overseeing implementation, monitoring progress, and making necessary course corrections
By honing their strategic skills, full-stack innovators ensure that their technological and creative efforts are directed towards achieving meaningful, long-term impact.
Growth (G)
The Growth dimension completes the TCSG Framework by focusing on the mindset and skills needed to scale impact and drive continuous improvement. It encompasses the ability to identify opportunities, adapt to changing conditions, and deliver measurable results.
Key components of the Growth dimension include:
Opportunity Identification: The aptitude for recognizing potential areas for growth, spotting possibilities for value creation, and identifying unmet needs and market gaps.
Results-Driven Orientation: A strong focus on achieving tangible outcomes, motivation from realizing measurable impact, and prioritization of quantifiable goals and metrics.
Adaptability: Openness and comfort with dynamic environments, ability to pivot nimbly in response to shifts, and resilience in the face of uncertainty.
Full-stack innovators cultivate their growth orientation through behaviors such as:
Actively seeking new markets, verticals, and opportunities to expand offerings and capabilities
Experimenting with innovative methods, tactics, and business models, and rapidly iterating based on results and feedback
Comprehensively gathering and analyzing data to measure impact and validate growth strategies
By developing their growth mindset and skills, full-stack innovators position themselves to drive sustainable expansion and create lasting value in their organizations and industries.
TCSG Overlaps and Combinations
While each dimension of the TCSG Framework is powerful in its own right, the true magic happens at the intersections.
Full-stack innovators excel at combining these dimensions to create synergies that lead to breakthrough innovations.
Let's explore some key overlaps:
Technology & Creativity (T&C): Innovative Design
At the intersection of Technology and Creativity, we find the realm of innovative design. This combination allows full-stack innovators to:
Develop cutting-edge, user-friendly solutions that push the boundaries of what's possible and desirable
Create immersive, interactive experiences that showcase emerging technologies
Apply creative coding techniques to solve complex problems in novel ways
Creativity & Strategy (C&S): Visionary Planning
The overlap of Creativity and Strategy enables full-stack innovators to:
Craft comprehensive brand strategies that align with shifting consumer preferences and market dynamics
Develop visionary product roadmaps that leverage emerging technologies and business models
Use design thinking principles to create long-term strategies that anticipate future trends and challenges
Strategy & Growth (S&G): Scalable Solutions
When Strategy meets Growth, full-stack innovators can:
Design modular, scalable architectures for rapidly growing platforms
Develop flexible, data-driven pricing strategies that optimize revenue growth and market penetration
Create adaptive business models that can evolve in response to changing market conditions
Growth & Technology (G&T): Data-Driven Optimization
The combination of Growth and Technology empowers full-stack innovators to:
Implement comprehensive growth hacking strategies leveraging AI-powered personalization and automation
Build robust experimentation platforms that enable rapid testing and iteration of growth hypotheses
Utilize advanced analytics to identify and capitalize on emerging market opportunities
Full-Stack Innovation: The Central Overlap (T&C&S&G)
At the heart of the TCSG Framework, where all four dimensions intersect, we find the essence of full-stack innovation.
This central overlap represents the pinnacle of cross-disciplinary expertise, enabling innovators to:
Lead the development of disruptive, AI-powered platforms that revolutionize entire industries
Spearhead the creation of groundbreaking, purpose-driven startups that solve critical societal challenges
Drive holistic, end-to-end innovation that creates transformative value and impact across multiple domains
By mastering these overlaps and combinations, full-stack innovators can tackle complex challenges from multiple angles, creating solutions that are not only technologically advanced and creatively designed but also strategically sound and primed for growth.
Developing TCSG Skills: A Roadmap for Full-Stack Innovators
Becoming a full-stack innovator requires mastery across all four dimensions of the TCSG Framework: Technology, Creativity, Strategy, and Growth. Let's explore how professionals can develop these skills, using a structured approach that acknowledges the unique components of each dimension.
The TCSG Framework outlines four levels of proficiency across each dimension:
Foundation: Basic understanding and application of TCSG skills in a limited context, with guidance and supervision.
Practitioner: Consistent demonstration of TCSG skills in real-world situations, with the ability to adapt and learn quickly.
Expert: Deep mastery of TCSG skills, with the ability to lead complex projects, innovate new approaches, and mentor others.
Visionary: Exceptional ability to combine TCSG skills in groundbreaking ways, shape industry trends, and create transformative impact at scale.
Let's break this down for each dimension:
Technology Dimension Proficiency Levels
Foundation: Understanding basic programming concepts, data analysis techniques, and emerging technology trends. Example: Ability to write simple scripts and perform basic data visualization.
Practitioner: Proficiency in multiple programming languages, advanced data analysis, and working knowledge of AI/ML concepts. Example: Developing full-stack web applications and implementing basic machine learning models.
Expert: Deep expertise in system architecture, advanced AI algorithms, and the ability to integrate multiple complex technologies. Example: Designing scalable, AI-powered platforms that leverage cloud computing and big data analytics.
Visionary: Pioneering new technological approaches that revolutionize industries. Example: Creating novel AI architectures that dramatically improve natural language processing capabilities.
Creativity Dimension Proficiency Levels
Foundation: Basic understanding of design thinking principles and ideation techniques. Example: Participating effectively in brainstorming sessions and generating multiple ideas for given problems.
Practitioner: Ability to apply creative problem-solving methods and design innovative solutions for complex challenges. Example: Leading design sprints and creating compelling user experiences for digital products.
Expert: Mastery in reframing complex problems and consistently generating breakthrough ideas. Example: Developing innovative business models that disrupt traditional industries.
Visionary: Ability to envision and articulate transformative future scenarios that shape entire fields. Example: Conceptualizing and initiating movements that redefine how society interacts with technology.
Strategy Dimension Proficiency Levels
Foundation: Understanding of basic strategic frameworks and ability to contribute to strategic discussions. Example: Conducting simple SWOT analyses and participating in goal-setting exercises.
Practitioner: Skill in developing comprehensive strategies and aligning teams around strategic objectives. Example: Creating detailed product roadmaps and go-to-market strategies.
Expert: Ability to craft and execute complex, multi-faceted strategies that drive significant organizational change. Example: Leading digital transformation initiatives across large enterprises.
Visionary: Capacity to develop groundbreaking strategies that reshape industries and create new markets. Example: Pioneering platform strategies that create entirely new ecosystems of value.
Growth Dimension Proficiency Levels
Foundation: Basic understanding of growth metrics and ability to execute simple growth experiments. Example: Running A/B tests on landing pages and analyzing basic user acquisition data.
Practitioner: Proficiency in developing and implementing comprehensive growth strategies across multiple channels. Example: Designing and managing full-funnel growth campaigns that significantly increase user acquisition and retention.
Expert: Mastery in scaling products and businesses, with the ability to identify and capitalize on new growth opportunities. Example: Leading international expansion efforts and developing new revenue streams for established products.
Visionary: Ability to drive exponential growth through innovative approaches that redefine how industries operate. Example: Creating viral growth loops that lead to rapid, global adoption of new technologies.
To progress along this roadmap, aspiring full-stack innovators should:
Assess Current Skills: Conduct a self-assessment across each TCSG dimension, identifying strengths and areas for improvement. For example, you might be a Practitioner in Technology, Foundation in Creativity, Foundation in Strategy, and Practitioner in Growth.
Set Development Goals: Based on the assessment, set specific, measurable goals for skill development in each dimension. For instance, aim to reach Practitioner level in Creativity by leading three design thinking workshops in the next six months.
Pursue Diverse Learning Opportunities: Engage in a mix of formal education, hands-on projects, mentorship, and self-directed learning to build TCSG skills. This could involve taking an AI course to boost your Technology skills, attending a strategic planning workshop to enhance your Strategy capabilities, or joining a startup accelerator to hone your Growth expertise.
Seek Cross-Disciplinary Experiences: Look for opportunities to work on projects that span multiple TCSG dimensions, pushing beyond comfort zones. For example, volunteer to lead a strategic initiative that requires both technological innovation and creative problem-solving.
Cultivate a Growth Mindset: Embrace challenges, learn from failures, and maintain a curiosity-driven approach to personal and professional development across all TCSG dimensions.
Implementing the TCSG Framework in Your Organization
Organizations can leverage the TCSG Framework to nurture full-stack innovators and drive innovation by focusing on each dimension's unique aspects:
Hiring and Talent Development: Use the TCSG dimensions as a guide for identifying and developing well-rounded innovators. For example:
Technology: Assess candidates' technical skills and ability to learn new technologies quickly.
Creativity: Evaluate problem-solving approaches and ability to generate innovative ideas.
Strategy: Look for systems thinking capabilities and long-term planning skills.
Growth: Assess data-driven decision-making abilities and adaptability to change.
Project Management: Implement a TCSG-based project management framework that ensures balanced consideration of all four dimensions throughout the innovation process. For instance:
Technology: Incorporate technical feasibility assessments and emerging tech trend analyses.
Creativity: Include design thinking workshops and user research phases.
Strategy: Embed strategic alignment checks and long-term impact evaluations.
Growth: Integrate growth modeling and scalability planning into project lifecycles.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Foster a culture that encourages collaboration across TCSG dimensions, breaking down silos between technical, creative, strategic, and growth-oriented teams. This could involve:
Creating cross-functional innovation squads that include members strong in each TCSG dimension.
Organizing regular knowledge-sharing sessions where experts from each dimension present insights to the broader organization.
Continuous Learning Programs: Develop training programs and learning opportunities that address all TCSG dimensions, helping employees broaden their skill sets. For example:
Technology: Offer coding bootcamps and AI/ML workshops.
Creativity: Provide design thinking certifications and innovation masterclasses.
Strategy: Organize business strategy simulations and scenario planning workshops.
Growth: Facilitate growth hacking seminars and data analytics courses.
Innovation Metrics: Create a balanced scorecard that measures innovation performance across TCSG dimensions, ensuring a holistic approach to value creation. This could include metrics such as:
Technology: Number of patents filed, technology adoption rates.
Creativity: Number of new ideas generated, user satisfaction scores.
Strategy: Long-term ROI of innovation initiatives, market share growth.
Growth: User acquisition rates, revenue growth from new products/services.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can create an environment that nurtures full-stack innovators and drives holistic innovation across all TCSG dimensions.
The Future of Work: TCSG and AI Augmentation
As AI continues to reshape the skills landscape, the TCSG Framework becomes increasingly relevant.
Full-stack innovators who master these dimensions will be well-positioned to:
Leverage AI as a Collaborator: Use AI tools to augment their capabilities across TCSG dimensions, from generating creative ideas to optimizing strategic decisions.
Drive Human-AI Synergy: Design innovative solutions that optimally combine human creativity and strategic thinking with AI's analytical and computational power.
Shape the Future of Industries: Lead the transformation of industries by reimagining business models, customer experiences, and operational processes in an AI-augmented world.
Navigate Ethical Challenges: Apply a multidimensional TCSG perspective to address the complex ethical considerations surrounding AI and emerging technologies.
Conclusion
The TCSG Framework provides a comprehensive roadmap for developing the diverse skill set needed to thrive as a full-stack innovator in the rapidly evolving landscape of business.
By cultivating expertise across the dimensions of Technology, Creativity, Strategy, and Growth – and learning to leverage the powerful synergies between them – professionals can position themselves at the forefront of innovation.
The ability to integrate these diverse skills will be more valuable than ever as time goes on. The challenges and opportunities presented by AI and other emerging technologies demand a new breed of innovator – one who can seamlessly navigate the complex interplay of technical expertise, creative vision, strategic insight, and growth-oriented execution.
I encourage you to reflect on your own TCSG skills, identify areas for growth, and embark on the exciting journey of becoming a full-stack innovator.
The future belongs to those who can harness the power of these interconnected dimensions to drive meaningful change and create lasting value in our ever-evolving world.